What is Aluminum Anodizing?
Aluminum anodizing is an electrochemical process in which an oxide (anodic) layer is chemically built on the
surface of the metal. This oxide layer acts as an insulator and can be dyed in a wide variety of colors. Anodizing
provides surface corrosion protection along with an excellent substrate for decorative finishes.
|

Photo courtesy of Global Metal Finishing
|
What is Hardcoat?
Hardcoat is a highly abrasion resistant, non-conductive aluminum oxide
(Al2O3-xH2O)
coating that makes an aluminum surface harder than tool steel due to greater thickness and weight than conventional
anodic coatings. Anodic coatings form an excellent base for dry film lubricants, Teflon, paint, and adhesives.
Note: You cannot hardcoat over hardcoat, anodize over anodize, build up hardcoat over anodize, chromic over
hardcoat, or just add another 0.0005" to the surface
|
Properties of Hardcoat
| Hardness | 65 to 70 Rockwell C, 850 to 900 DPH, harder than hard chrome plate |
| Color | Dark Gray to Black |
| Coating Thickness | 0.002" average, 0.015" for salvage purposes on selected alloys |
| Dielectric | Hardcoat is non-conductive and will withstand 800 volts per 0.001" thickness. |
| Machining | Hardcoat can be ground, lapped, honed or polished. |
| Dyeing | Hardcoat may be dyed most colors but tends to come out dark. |
| Sealing | Hardcoat may be Dichromate, Ni-Acetate, hot water, or Teflon sealed. |
| Resistivity | between 106 to 1012 Ohm-cm |
|
Design ConsiderationsAvoid the following when designing for an
anodized finish:
- blind holes
- hollow weldments
- steel inserts
- sharp corners
- heavy to thin cross sections
| Coating Thickness vs. Corner Radius
| Nominal Coating Thickness, inch |
Radius on edge & inside corner |
| 0.001 |
~ 1/32 inch |
| 0.002 |
~ 1/16 inch |
| 0.003 |
~ 3/32 inch |
| 0.004 |
~ 1/8 inch |
|
What is Chemical Conversion?
also known as: Chem Film, Irridite, Alodine, ChemTreat
Chemical conversion coatings are intended to prevent corrosion, improve
adhesion of paint finish or other coatings, and for improved electrical and electronic
applications where low resistance contacts are required. The primary
difference between a Class 1A and Class 3 coating is thickness, since current
passes more readily through a thinner current resistant barrier (coating).
Class 3 is thinner. | 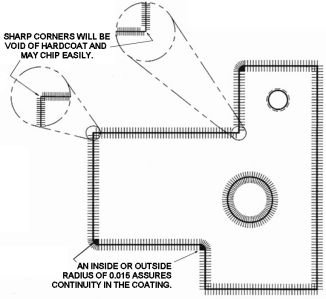 |
Weldments and Welded aluminum parts
When two or more parts are welded together, acid is entrapped in the weld and
the area around the weld. Color variations exist when a welding rod alloy
is vastly different from the alloy used to make the part. Halos appear
around welds because of the high temperature used in the welding process.
The area around the weldment will be slightly lighter in color, causing the
welded area to appear larger than it is. |
Masking
Masking is required where no build up is desired or when a part needs both anodizing & chemical conversion. All threaded holes, 1/4" or smaller, are typically masked when hardcoating unless otherwise specified. Holes with heli-coils
must be masked. Any dissimilar metal (steel, brass, bronze) or any form of
plating will burn off in the anodizing tank unless masked. |
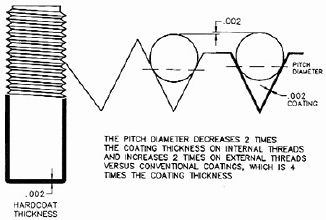
Hardcoat and Thread CoatingHardcoat thickness is typically
0.002" (0.0508 mm). Half the coating thickness is build-up and half is
penetration into the base metal. For the threaded rod on the right, the
diameter increased by 0.002" since half of the coating thickness (0.001") built
up the diameter on each side of the rod. |
 |
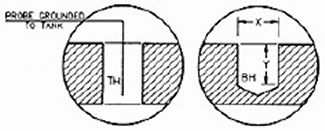
Hardcoat Blind Holes or Through HolesThrough holes (TH on
drawing at right) will hardcoat evenly up to twice the length of the diameter
(X).
Blind holes (BH on drawing at right) will only hardcoat to a depth equal to the
diameter of the hole (X=Y).
|  |
Coating Thickness, Color and Alloys
See chart at right. Example: Alloy 2024 may have a max. coating
thickness of 0.005" and will be gray in color.
++Note: Coatings over 0.0035" tend to chip and become milky in color and
should only be used in the salvage of parts. | 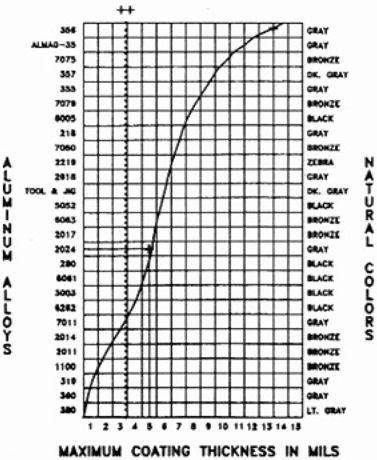 |
Annodizing design guide provided by Anodic, Inc.
